In this article, we try to provide Symbolic Links guide steps in Linux for beginners. You will learn to create, enable, disable, and remove symbolic links in Linux distributions. In Linux, a symbolic link (also known as a symlink) is a type of file that serves as a reference or pointer to another file or directory. It’s similar to a shortcut in Windows. A symlink can point to a file or a directory on the same or a different filesystem.
Important Notes To Symlinks in Linux
Before you start, you need to know the following notes about symlinks:
- Reference by Path: A symbolic link points to a file or directory by its path. If the target is moved or renamed, the symlink will not update and will point to a non-existent location and become a broken link.
- Not a Copy: The symlink is not a copy of the target file; it’s simply a pointer. Any changes made to the file through the symlink are made to the target file.
- Storage and Permissions: A symbolic link has its file permissions, but these permissions do not affect access to the target file. Access permissions are determined by the target file’s permissions.
- File Size: The size of a symbolic link is the number of characters in the path it points to, not the size of the actual target file.
A Comprehensive Guide of Symbolic Links in Linux For Beginners
For learning Symbolic links, you need a Linux distro such as Debian, Ubuntu, AlmaLinux, etc, and root or non-root user access with sudo privileges.
Then, follow the steps below to complete this guide. Here we use AlmaLinux distro to show you the guide steps.
Step 1 – Create or Add a Symlink on Linux
To create a symlink, you can easily use the ln command with the -s option. The format of it looks like the following command:
ln -s target_path link_name
The target path is the path to the file or directory you want to link to. The link name is the path of the symbolic link you’re creating.
For example:
ln -s /usr/local/example.txt ~/example_link.txt
This command creates a symbolic link named example_link.txt in the user’s home directory, which points to /usr/local/example.txt.
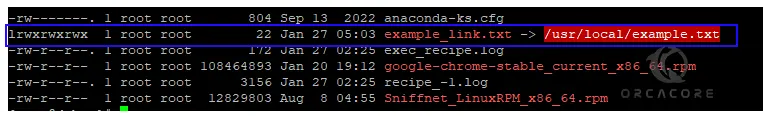
Also, you can use the ls -la to get full information and permissions to your symlinks.
ls -laExmaple Output
...
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 22 Jan 27 05:03 example_link.txt -> /usr/local/e xample.txt
Step 2 – Disable a Symlink in Linux
At this point, you can easily disable your symbolic links. It depends on the web server that you are using.
Apache users can add the following line to the .htaccess or the Apache configuration file to disable a symbolic link:
Options -FollowSymlinksNginx users can use the following line in their configuration files to disable a symbolic link:
disable_symlinks onStep 3 – Unlink or Remove a Symbolic Link in Linux
If you plan to remove or unlink a symlink on your distro, you can simply use the following commands:
# rm link_name
Or
# unlink link_nameFor example:
# rm example_link.txt
Or
# unlink example_link.txt
Note: If you are unsure whether a file is a symbolic link, you can use the ls -l command to check it. Symbolic links are indicated with an l (lowercase L) in the first column of the output, and the link path is shown after the -> symbol.
For example:

Step 4 – Find Broken Symbolic Links in Linux
As you may know, a broken link is the target of a link that doesn’t exist. To find a broken link in Linux, you can use the find command with the -xtype l option:
find /path/to/search -xtype l
Replace the /path/to/search with the desired directory you want to search for broken links. Also, you can use / to search your entire system.
For example, to find all broken symbolic links in the home directory, we can use:
find ~/ -xtype lThe command will show a list of broken symbolic links found in the specified directory and its subdirectories.
Conclusion
AppArmor Configuration on Debian 12 Bookworm
Best Way To Get PHP 7.4 on Debian 12 Bookworm
Extract Tar Gz Files in the Linux Command Line
Fix unknown filesystem type NTFS error in Linux
Essential Facts About /etc/passwd File in Linux


